Delaware Bay, Delaware Benthic Habitats 2010 Substrate
Data Set (DS) | Office for Coastal Management (OCM)GUID: gov.noaa.nmfs.inport:47870 | Updated: May 30, 2023 | Published / External
Item Identification
| Title: | Delaware Bay, Delaware Benthic Habitats 2010 Substrate |
|---|---|
| Short Name: | de_db10-substrate_Metadata |
| Status: | Completed |
| Publication Date: | 2015 |
| Abstract: |
The Coastal Program of Delaware's Division of Soil and Water conservation (DNREC), the University of Delaware, Partnership for the Delaware Estuary, and the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection have partnered and are carrying out a bottom and sub-bottom imaging project to identify and map the benthic habitat and sub-bottom sediments of Delaware Bay and River. This project was initiated to better understand the distribution of bottom sediment types, habitat biodiversity, and most importantly, human's impact on the bay bottom and its living resources. The project integrates the use of three types of acoustical systems: Roxann Seabed classification system, chirp sub-bottom profiling, and multi-beam bathymetric mapping. Verification of the acoustic data with bottom and sub-bottom sediments is performed through the collection of bra banc core samples and underwater video images. Original contact information: Contact Org: NOAA Office for Coastal Management Phone: 843-740-1202 Email: coastal.info@noaa.gov |
| Purpose: |
The Delaware Bay project has four principle goals. The first is to determine the location and extent of oyster reef habitats in upper Delaware Bay which will greatly improve the ability of Delaware and New Jersey to manage these commercial resources. The second goal is to evaluate short-nose, and atlantic sturgeon habitat. Sturgeon in the bay have shown an affinity for certain regions within the system. A better understanding of the conditions in these areas would improve the ability to assess the impact of dredging or other activities. A third goal was to identify potential borrow sites for beach re-nourishment materials. Finally, the high-resolution bathymetry collected in the bay will improve the understanding of sediment movement and other human impacts on the bay |
| Notes: |
10027 |
Keywords
Theme Keywords
| Thesaurus | Keyword |
|---|---|
| Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Science Keywords |
EARTH SCIENCE > BIOSPHERE > ECOSYSTEMS > MARINE ECOSYSTEMS > BENTHIC
|
| Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Science Keywords |
EARTH SCIENCE > BIOSPHERE > ECOSYSTEMS > MARINE ECOSYSTEMS > COASTAL
|
| Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Science Keywords |
EARTH SCIENCE > BIOSPHERE > ECOSYSTEMS > MARINE ECOSYSTEMS > ESTUARY
|
| ISO 19115 Topic Category |
environment
|
| UNCONTROLLED | |
| None | Benthic Habitat |
| None | Bottom Sediments |
| None | CMECS |
| None | Coastal and Marine Ecological Classification Standard |
| None | Environmental Monitoring |
| None | SAV |
| None | Shellfish Beds |
| None | Substrate Component |
Spatial Keywords
| Thesaurus | Keyword |
|---|---|
| Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Location Keywords |
CONTINENT > NORTH AMERICA > UNITED STATES OF AMERICA > DELAWARE
|
| UNCONTROLLED | |
| None | Delaware |
| None | Delaware Bay |
| None | Delaware River |
| None | State of Delaware |
| None | State of New Jersey |
| None | USA |
Stratum Keywords
| Thesaurus | Keyword |
|---|---|
| UNCONTROLLED | |
| None | Sediment Water Interface |
| None | Surface Sediment Mapping |
Physical Location
| Organization: | Office for Coastal Management |
|---|---|
| City: | Charleston |
| State/Province: | SC |
Data Set Information
| Data Set Scope Code: | Data Set |
|---|---|
| Maintenance Frequency: | As Needed |
| Data Presentation Form: | Map (digital) |
| Distribution Liability: |
NOAA provides no warranty, nor accepts any liability occurring from any incomplete, incorrect, or misleading data, or from any incorrect, incomplete, or misleading use of the data. It is the responsibility of the user to determine whether or not the data is suitable for the intended purpose. |
Support Roles
Data Steward
| Date Effective From: | 2015 |
|---|---|
| Date Effective To: | |
| Contact (Organization): | NOAA Office for Coastal Management (NOAA/OCM) |
| Address: |
2234 South Hobson Ave Charleston, SC 29405-2413 |
| Email Address: | coastal.info@noaa.gov |
| Phone: | (843) 740-1202 |
| URL: | https://coast.noaa.gov |
Distributor
| Date Effective From: | 2015 |
|---|---|
| Date Effective To: | |
| Contact (Organization): | NOAA Office for Coastal Management (NOAA/OCM) |
| Address: |
2234 South Hobson Ave Charleston, SC 29405-2413 |
| Email Address: | coastal.info@noaa.gov |
| Phone: | (843) 740-1202 |
| URL: | https://coast.noaa.gov |
Metadata Contact
| Date Effective From: | 2015 |
|---|---|
| Date Effective To: | |
| Contact (Organization): | NOAA Office for Coastal Management (NOAA/OCM) |
| Address: |
2234 South Hobson Ave Charleston, SC 29405-2413 |
| Email Address: | coastal.info@noaa.gov |
| Phone: | (843) 740-1202 |
| URL: | https://coast.noaa.gov |
Point of Contact
| Date Effective From: | 2015 |
|---|---|
| Date Effective To: | |
| Contact (Organization): | NOAA Office for Coastal Management (NOAA/OCM) |
| Address: |
2234 South Hobson Ave Charleston, SC 29405-2413 |
| Email Address: | coastal.info@noaa.gov |
| Phone: | (843) 740-1202 |
| URL: | https://coast.noaa.gov |
Extents
| Currentness Reference: | Ground Condition |
|---|
Extent Group 1
Extent Group 1 / Geographic Area 1
| W° Bound: | -75.6056 | |
|---|---|---|
| E° Bound: | -75.16708 | |
| N° Bound: | 39.83218 | |
| S° Bound: | 38.80217 |
Extent Group 1 / Time Frame 1
| Time Frame Type: | Range |
|---|---|
| Start: | 2004 |
| End: | 2010 |
Spatial Information
Spatial Representation
Representations Used
| Vector: | Yes |
|---|
Access Information
| Security Class: | Unclassified |
|---|---|
| Data Access Constraints: |
Public Information |
| Data Use Constraints: |
None |
Distribution Information
Distribution 1
| Download URL: | ftp://ftp.coast.noaa.gov/pub/benthic/Benthic_Cover_Data/DE_DelawareBay.zip |
|---|---|
| Distributor: | |
| File Name: | Bulk Download |
| Description: |
FTP download of data files. |
URLs
URL 1
| URL: | https://iocm.noaa.gov/cmecs |
|---|---|
| Name: | CMECS Home Page |
| URL Type: |
Online Resource
|
| Description: |
Information and resources on the CMECS standard and how to apply it |
URL 2
| URL: | http://www.cmecscatalog.org/ |
|---|---|
| Name: | CMECS Catalog |
| URL Type: |
Online Resource
|
| Description: |
Searchable online catalog of CMECS units, descriptions, and source references |
URL 3
| URL: | https://coast.noaa.gov/digitalcoast/ |
|---|---|
| Name: | NOAA's Office for Coastal Management (OCM) Digital Coast Data section |
| URL Type: |
Online Resource
|
| Description: |
The website provides not only coastal data, but also the tools, training, and information needed to make these data truly useful. Content comes from many sources, all of which are vetted by NOAA. |
URL 4
| URL: | https://coast.noaa.gov/ |
|---|---|
| Name: | NOAA's Office for Coastal Management (OCM) website |
| URL Type: |
Online Resource
|
| Description: |
Information on the NOAA Office for Coastal Management (OCM) |
URL 5
| URL: | https://coast.noaa.gov/data/Images/Collections/BenthicCover_thumbnail.jpg |
|---|---|
| Name: | Browse Graphic |
| URL Type: |
Browse Graphic
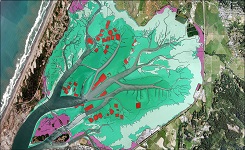
|
| File Resource Format: | JPEG |
| Description: |
Sample of benthic cover data |
Activity Log
Activity Log 1
| Activity Date/Time: | 2017-03-30 |
|---|---|
| Description: |
Date that the source FGDC record was last modified. |
Activity Log 2
| Activity Date/Time: | 2017-11-14 |
|---|---|
| Description: |
Converted from FGDC Content Standard for Digital Geospatial Metadata (version FGDC-STD-001-1998) using 'fgdc_to_inport_xml.pl' script. Contact Tyler Christensen (NOS) for details. |
Activity Log 3
| Activity Date/Time: | 2018-04-11 |
|---|---|
| Description: |
Partial upload to move data access FTP links to Distribution Info and remove broken URLs. |
Data Quality
| Completeness Report: |
Very shallow areas within the Delaware River/Bay system were not surveyed due to access limitations. |
|---|---|
| Conceptual Consistency: |
Ground truth information was collected at the time of the original surveys to calibrate the mapping and ensure the accuracy of the habitat designations. |
Lineage
Sources
Delaware Bay Benthic Mapping Project
| Contact Name: | Coastal Program of Delaware's Division of Soil and Water Conservation (DNREC) |
|---|---|
| Publish Date: | 2010-01-01 |
| Extent Type: | Range |
| Extent Start Date/Time: | 2004 |
| Extent End Date/Time: | 2010 |
| Source Contribution: |
This is a compilation of several habitat data sets collected through a variety of methods. | Type of Source Media: CD-ROM |
Process Steps
Process Step 1
| Description: |
Bivalve Reef (Oyster, Identified Oyster, and Corbicula) polygons were derived from the bottom sediment map that were constructed by the utilization of a Roxann Seabed Classification System and extensive sediment grab samples bottom sediment map that were constructed by the utilization of a Roxann Seabed Classification System and extensive sediment grab samples. Corbicula fluminea beds were identified on the Roxann output by the occurrence of data point which had moderate to high hardness return (E2) and an anomalously high roughness return (E1), as compared to the adjacent sediments. The sediments surrounding these beds are usually of a finer (silt to clay) grain size, with low roughness and hardness values. The regions where these types of returns were encountered were then sampled with a grab sampler. Several samples (2 to 3 samples) were collected at each station to increase the likely hood that Corbicula would be encountered, if it was indeed located in that region. Corbicula beds can have varying densities, distributions, and bed configurations; hence this sampling scheme was enacted to account for this spatial variability. Submersed Rooted Vascular Plants (Vallisneria Americana) beds outlines were identified through the same bottom sediment map used for delineating bivalve reef. SRV beds were identified on the Roxann output by the occurrence of data point which had very low hardness returns (E2) and an anomalously high roughness return (E1), as compared to the adjacent sediments. The regions where these types of returns were encountered, where then sampled with a grab sampler. Several samples (2 to 3 samples) were collected at each station to increase the likely hood that SAV would be encountered, if it was indeed located in that region. SAV beds can have varying densities, distributions, and bed configurations; hence the sampling scheme was enacted to account for this spatial variability. Outcrop areas consist of Cretaceous sediment that is at the river bottom surface (or near the surface ~1 to 2 cm). These areas are scour or erosional zones within the river. The outcropping material consists of highly compacted/de-watered silty fine sand to fine sandy silts, which contain relict burrow casts and glauconite. Outcrop boundaries were derived from the bottom sediment map raster grid. |
|---|---|
| Process Date/Time: | 2008-01-01 00:00:00 |
Process Step 2
| Description: |
The bottom sediment map was constructed by the utilization of a Roxann Seabed Classification System and extensive sediment grab samples. Data was collected in a gridded trackline configuration, with tracklines spacing of 100 meters parallel to the shoreline and 200 meters perpendicular to the shoreline. This project is an extension of the work currently being performed in Delaware waters by DNREC's Delaware Coastal Program's Delaware Bay Benthic Mapping Project. The bottom sediment point data, which has been classified according to the existing benthic mapping Roxann box plot, are converted from a number that categorizes the point according to its corresponding box (in the Roxann) into a number which reflects the sediment properties of each box in relation to one another. A ranking scale is used to allow a statistical gridding scheme to interpolate between sediment data points, while minimizing erroneous sediment classifications and allowing gradational sediment deposits to be gridded. A ranking scale from 0 to 28 was used for this project, with 0 representing the finest grained classifications (fluidized clay) and 28 representing the coarsest grained classifications (dense shell material). Table 1 illustrates the distribution of sediment classifications along the ranking scale, which takes into account the relation of sediment types and grain sizes to one another using both the Wentworth Scale and Shepard's classification system. Finer grains are more similar in their deposition environments, such as clay and silts, because they reflect similar current regimes, sorting, and reworking patterns (Poppe et al., 2003). While coarse sediments are much more dissimilar to finer grains, with respect to current velocities, sorting, and winnowing, the finer grains are much more closely related in their sediment diameters that the coarser grains as you increase in Phi size and/or diameter. These account for the close clustering of coarse grained deposit descriptions at the upper end of the ranking scale, while the finer grained sediments show a gradation as you increase in the rating scale. |
|---|---|
| Process Date/Time: | 2008-01-01 00:00:00 |
Process Step 3
| Description: |
The bottom sediment data is gridded in Surfer degrees 8, a surface and terrain modeling program, using block kriging and a nugget effect. This statistical griding technique estimates the average value of a variable within a prescribed local area (Isaaks and Srivastava, 1989). Block kriging utilizes the existing point data values, weights the values of the data depending upon the proximity to the point being estimated, to discretize the local area into an array of estimated data value points and then averaging those individual point estimates together to get an average estimated value over the area of interest (Isaaks and Srivastava, 1989). A variogram is constructed for the data, and the resultant spatial model that is developed from the variogram is used in the block kriging surface model to more accurately interpolate the sediment data . The fitted model was a nugget effect (with an error variance of 21.8%) and a linear model (with a slope of 0.00286 and an anisotropy of 1, which represents a complete lack of spatial correlation).The accuracy of the estimation is dependent upon the grid size of the area of interpolation, the size of each cell within the grid, and the number of discretized data points that are necessary to estimate the cells within that grid spacing. The grid size that was used to interpolate the bottom sediment maps was 442 lines x 454 lines, with a cell size of 44.93 m2. The nugget effect is added to allow the griding to assume there is very little, if any, lateral correlation or trends within the bottom sediment (Isaaks and Srivastava, 1989). The nugget effect model entails a complete lack of spatial correlation; the point data values at any particular location bear no similarity even to adjacent data values (Isaaks and Srivastava, 1989). Without the nugget effect the gridding would assume that you could only have a linear progression of sediment types and would insert all the sediment types along the scale between two sediment types (i.e. silty fine to medium sands and fine to medium sand with varying amounts of pebbles would be inserted between fine sand and coarse sand even though that is not what is occurring along the bottom. The sediment data is gridded with no drift for the data interpolation, also helping to minimize erroneous classifications. Sediment Classification Ranking Sediment Description 0-11-2 Clay, 2-33-44-55-66-7 Silt,7-88-9 Sandy Silts, 9-1010-11 Fine Sand, 11-1212-13 Silty Fine to Medium Sands, 13-14 Silty Medium Sand, 14-1515-16 Fine to Medium Sand, 16-1717-18 Fine to Medium Sand with abundant shell material and/or pebbles, 18-1919-20 Coarse Sand with varying amounts of pebbles, 20-2121-2222-23 Moderate Shell Material/Sandy Pebbles, 23-2424-2525-26 Abundant Shell Material/Gravel, 26-2727-28 Dense Oyster Shell. |
|---|---|
| Process Date/Time: | 2008-01-01 00:00:00 |
Process Step 4
| Description: |
Separate shapefiles for oyster beds, identified oyster beds, SAV, corbicula, outcroppings, and depositional zones were integrated into a single feature layer to produce a comprehensive benthic cover polygon data set using the ArcMap 10 Merge tool. A review of the bottom sediment raster data sets (Delaware River/Bay, Upper Shelf, and Roxann 2004 which lies along the Delaware near-shore area) indicated that they consisted entirely of various types of unconsolidated sediments ranging from fluidized clay to oyster shells. Each of these rasters were converted into a single Unconsolidated Sediments polygon layer, merged together and then joined with the other features (oyster, SAV, etc.) to form a continuous benthic cover layer for the entire project area. As a final step habitat classes from the Florida System for Classifying Habitats in Estuarine and Marine Environments (SCHEME) were added to the attribute table for this single polygon file to ensure consistency with other Digital Coast benthic cover data sets. |
|---|---|
| Process Date/Time: | 2012-01-01 00:00:00 |
Process Step 5
| Description: |
The bottom sediment maps (source for the unconsolidated sediments polygons in the vector data set) were constructed by the utilization of a Roxann Seabed Classification System and extensive sediment grab samples. Data was collected in a gridded trackline configuration, with tracklines spacing of 100 meters parallel to the shoreline and 200 meters perpendicular to the shoreline.This project is an extension of the work currently being performed in Delaware waters by DNREC's Delaware Coastal Program's Delaware Bay Benthic Mapping Project.The bottom sediment point data, which has been classified according to the existing benthic mapping Roxann box plot, are converted from a number that categorizes the point according to its corresponding box (in the Roxann) into a number which reflects the sediment properties of each box in relation to one another. A ranking scale is used to allow a statistical griding scheme to interpolate between sediment data points, while minimizing erroneous sediment classifications and allowing gradational sediment deposits to be gridded. A ranking scale from 0 to 28 was used for this project, with 0 representing the finest grained classifications (fluidized clay) and 28 representing the coarsest grained classifications (dense shell material). This ranking scale takes into account the relation of sediment types and grain sizes to one another using both the Wentworth Scale and Shepard's classification system. Finer grains are more similar in their deposition environments, such as clay and silts, because they reflect similar current regimes, sorting, and reworking patterns (Poppe et al., 2003). While coarse sediments are much more dissimilar to finer grains, with respect to current velocities, sorting, and winnowing, the finer grains are much more closely related in their sediment diameters that the coarser grains as you increase in Phi size and/or diameter. These account for the close clustering of coarse grained deposit descriptions at the upper end of the ranking scale, while the finer grained sediments show a gradation as you increase in the rating scale. |
|---|---|
| Process Date/Time: | 2012-01-01 00:00:00 |
Process Step 6
| Description: |
The bottom sediment data is gridded in Surfer degrees 8, a surface and terrain modeling program, using block kriging and a nugget effect. This statistical griding technique estimates the average value of a variable within a prescribed local area (Isaaks and Srivastava, 1989). Block kriging utilizes the existing point data values, weights the values of the data depending upon the proximity to the point being estimated, to discretize the local area into an array of estimated data value points and then averaging those individual point estimates together to get an average estimated value over the area of interest (Isaaks and Srivastava, 1989). A variogram is constructed for the data, and the resultant spatial model that is developed from the variogram is used in the block kriging surface model to more accurately interpolate the sediment data . The fitted model was a nugget effect (with an error variance of 21.8%) and a linear model (with a slope of 0.00286 and an anisotropy of 1, which represents a complete lack of spatial correlation).The accuracy of the estimation is dependent upon the grid size of the area of interpolation, the size of each cell within the grid, and the number of discretized data points that are necessary to estimate the cells within that grid spacing. The grid size that was used to interpolate the bottom sediment maps was 442 lines x 454 lines, with a cell size of 44.93 m2. The nugget effect is added to allow the griding to assume there is very little, if any, lateral correlation or trends within the bottom sediment (Isaaks and Srivastava, 1989). The nugget effect model entails a complete lack of spatial correlation; the point data values at any particular location bear no similarity even to adjacent data values (Isaaks and Srivastava, 1989). Without the nugget effect the griding would assume that you could only have a linear progression of sediment types and would insert all the sediment types along the scale between two sediment types (i.e. silty fine to medium sands and fine to medium sand with varying amounts of pebbles would be inserted between fine sand and coarse sand even though that is not what is occurring along the bottom. The sediment data is gridded with no drift for the data interpolation, also helping to minimize erroneous classifications. Sediment Classification Ranking Sediment Description: 0-11-2 Clay, 2-33-44-55-66-7 Silt, 7-88-9 Sandy Silts, 9-1010-11 Fine Sand, 11-1212-13 Silty Fine to Medium Sands, 13-14 Silty Medium Sand, 14-1515-16 Fine to Medium Sand, 16-1717-18 Fine to Medium Sand, with abundant shell material and/or pebbles, 18-1919-20 Coarse Sand, with varying amounts of pebbles 20-2121-2222-23 Moderate Shell Material / Sandy Pebbles, 23-2424-2525-26 Abundant Shell Material / Gravel 26-2727-28 Dense Oyster Shell |
|---|---|
| Process Date/Time: | 2012-01-01 00:00:00 |
Process Step 7
| Description: |
The data were converted from a single ESRI polygon shapefile classified according to the System for Classifying Habitats in Estuarine and Marine Environments (SCHEME) to the Coastal and Marine Ecological Classification Standard (CMECS) 2012 format (which can be found at https://coast.noaa.gov/digitalcoast/tools/cmecs-crosswalk) which produces separate geoform, substrate, and substrate feature layers from the original input benthic habitat dataset. This substrate feature layer contains CMECS substrate component attributes where an "Equal" or "Nearly Equal" SCHEME value was present in the original data. Polygons for which no substrate information was present have been removed. No other changes to the original polygon boundaries or any other alterations of the original SCHEME data were made during this process. |
|---|---|
| Process Date/Time: | 2015-01-01 00:00:00 |
Catalog Details
| Catalog Item ID: | 47870 |
|---|---|
| GUID: | gov.noaa.nmfs.inport:47870 |
| Metadata Record Created By: | Anne Ball |
| Metadata Record Created: | 2017-11-14 12:57+0000 |
| Metadata Record Last Modified By: | SysAdmin InPortAdmin |
| Metadata Record Last Modified: | 2023-05-30 18:09+0000 |
| Metadata Record Published: | 2018-04-11 |
| Owner Org: | OCM |
| Metadata Publication Status: | Published Externally |
| Do Not Publish?: | N |
| Metadata Last Review Date: | 2018-04-11 |
| Metadata Review Frequency: | 1 Year |
| Metadata Next Review Date: | 2019-04-11 |
